Force and motion¶
Force¶
Describes interactions between two objects or an object and environment.
Newtons Laws gives us an toolkit how to handle these interactions.
Types of forces¶
contact (Between two objects)
normal force (\(\vec{n}\)) object rests on a surface the normal force is perpendicular to the surface (surface pushes the object upwards)
friction (\(\vec{f}\)) acts parallel to the surface (if we slide something there is friction, it is always opposite to the direction it moves)
tension (\(\vec{t}\)) force applied to an object pulled by a rope
weight (\(\vec{v}\)) gravitational attraction
Resultant of force (super position of forces)¶
If two forces act on the same object at the same time, the effect is the same as if a single force would act.
\[
\vec{R} = \vec{F}_1 + \vec{F}_2
\]
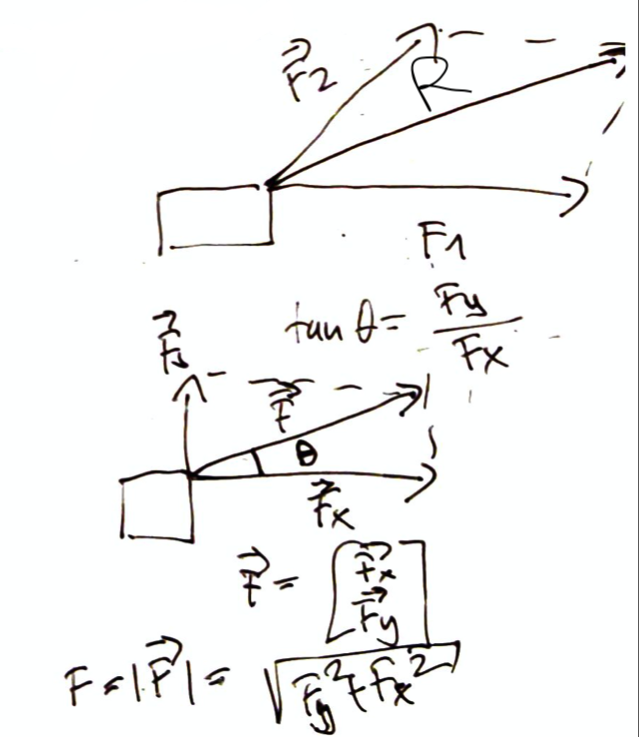
We can express any force by its components:
\[\begin{split}
\vec{R} = \vec{F}_1 + \vec{F}_2 + \cdots = \sum \vec{F} \\
R_x = \sum \vec{F}_x \\
R_y = \sum \vec{F}_y
\end{split}\]
