Probability chain rule¶
Let \(S_1, \cdots, S_k\) be events \(P(S_i) > 0\) then the chain rule states:
\[
P(S_1 , S_2 , \cdots , S_k) = P(S_1)P(S_2|S_1)P(S_3|S_2 , S_1) \cdots P(S_k| S_1 , S_2 , \cdots , S_{k-1})
\]
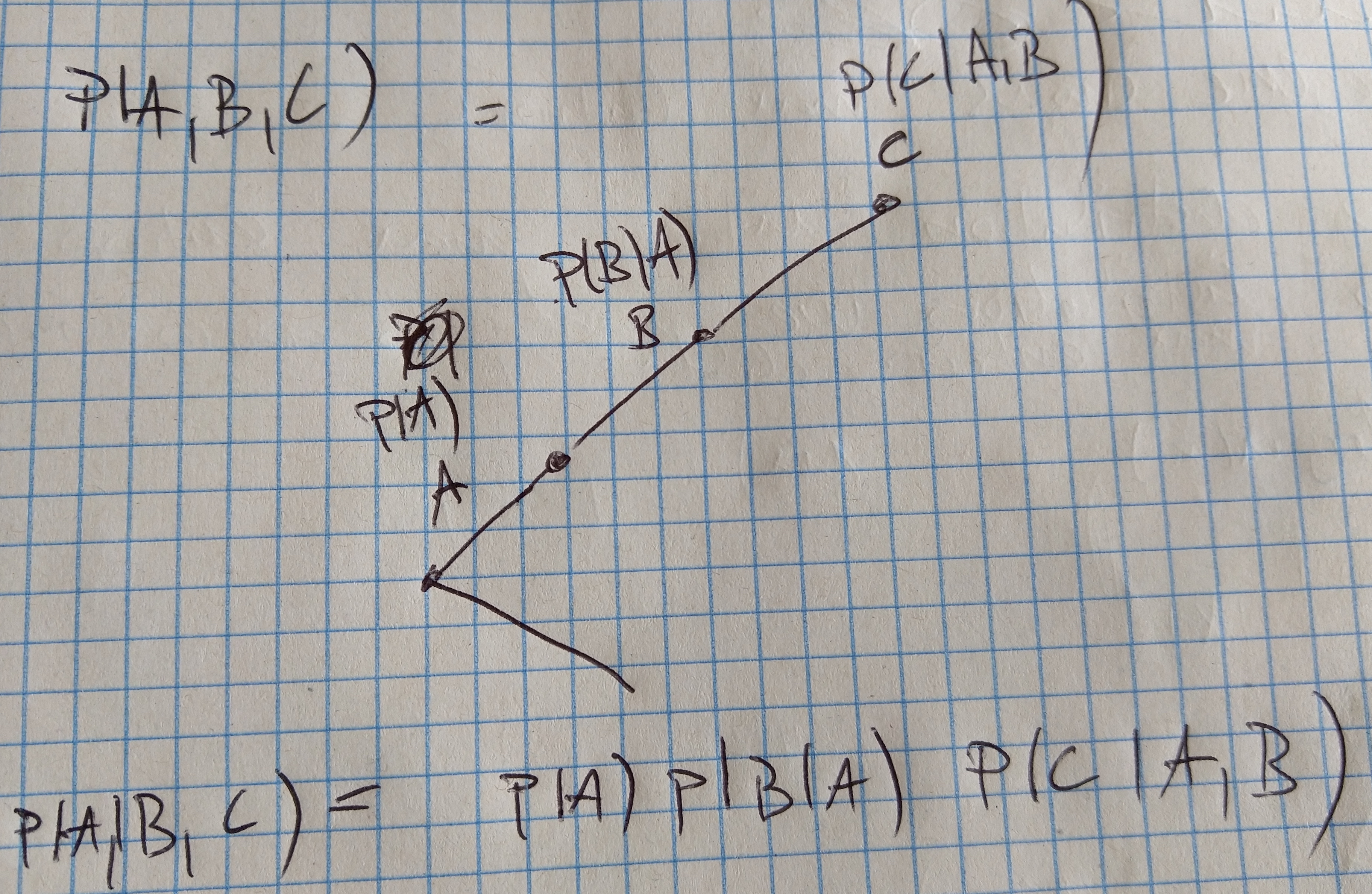
Expressing conditional distribution \(p(S_k| S_{1:k-1})\) gets complicated as k grows larger. To express the join distribution of C states and K variables variables we need \(O(C^K)\) observations. We can model this distribution using conditional probability tables (CPT) .
